$\require{mathtools}
\newcommand{\nc}{\newcommand}
%
%%% GENERIC MATH %%%
%
% Environments
\newcommand{\al}[1]{\begin{align}#1\end{align}} % need this for \tag{} to work
\renewcommand{\r}{\mathrm} % BAD!! does cursed things with accents :((
\renewcommand{\t}{\textrm}
\newcommand{\either}[1]{\begin{cases}#1\end{cases}}
%
% Delimiters
% (I needed to create my own because the MathJax version of \DeclarePairedDelimiter doesn't have \mathopen{} and that messes up the spacing)
% .. one-part
\newcommand{\p}[1]{\mathopen{}\left( #1 \right)}
\renewcommand{\P}[1]{^{\p{#1}}}
\renewcommand{\b}[1]{\mathopen{}\left[ #1 \right]}
\newcommand{\lopen}[1]{\mathopen{}\left( #1 \right]}
\newcommand{\ropen}[1]{\mathopen{}\left[ #1 \right)}
\newcommand{\set}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\{ #1 \right\}}
\newcommand{\abs}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\lvert #1 \right\rvert}
\newcommand{\floor}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\lfloor #1 \right\rfloor}
\newcommand{\ceil}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\lceil #1 \right\rceil}
\newcommand{\round}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\lfloor #1 \right\rceil}
\newcommand{\inner}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\langle #1 \right\rangle}
\newcommand{\norm}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\lVert #1 \strut \right\rVert}
\newcommand{\frob}[1]{\norm{#1}_\mathrm{F}}
\newcommand{\mix}[1]{\mathopen{}\left\lfloor #1 \right\rceil}
%% .. two-part
\newcommand{\inco}[2]{#1 \mathop{}\middle|\mathop{} #2}
\newcommand{\co}[2]{ {\left.\inco{#1}{#2}\right.}}
\newcommand{\cond}{\co} % deprecated
\newcommand{\pco}[2]{\p{\inco{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\bco}[2]{\b{\inco{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\setco}[2]{\set{\inco{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\at}[2]{ {\left.#1\strut\right|_{#2}}}
\newcommand{\pat}[2]{\p{\at{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\bat}[2]{\b{\at{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\para}[2]{#1\strut \mathop{}\middle\|\mathop{} #2}
\newcommand{\ppa}[2]{\p{\para{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\pff}[2]{\p{\ff{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\bff}[2]{\b{\ff{#1}{#2}}}
\newcommand{\bffco}[4]{\bff{\cond{#1}{#2}}{\cond{#3}{#4}}}
\newcommand{\sm}[1]{\p{\begin{smallmatrix}#1\end{smallmatrix}}}
%
% Greek
\newcommand{\eps}{\epsilon}
\newcommand{\veps}{\varepsilon}
\newcommand{\vpi}{\varpi}
% the following cause issues with real LaTeX tho :/ maybe consider naming it \fhi instead?
\let\fi\phi % because it looks like an f
\let\phi\varphi % because it looks like a p
\renewcommand{\th}{\theta}
\newcommand{\Th}{\Theta}
\newcommand{\om}{\omega}
\newcommand{\Om}{\Omega}
%
% Miscellaneous
\newcommand{\LHS}{\mathrm{LHS}}
\newcommand{\RHS}{\mathrm{RHS}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\cst}{const}
% .. operators
\DeclareMathOperator{\poly}{poly}
\DeclareMathOperator{\polylog}{polylog}
\DeclareMathOperator{\quasipoly}{quasipoly}
\DeclareMathOperator{\negl}{negl}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{arg\thinspace min}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{arg\thinspace max}
\DeclareMathOperator{\diag}{diag}
% .. functions
\DeclareMathOperator{\id}{id}
\DeclareMathOperator{\sign}{sign}
\DeclareMathOperator{\step}{step}
\DeclareMathOperator{\err}{err}
\DeclareMathOperator{\ReLU}{ReLU}
\DeclareMathOperator{\softmax}{softmax}
% .. analysis
\let\d\undefined
\newcommand{\d}{\operatorname{d}\mathopen{}}
\newcommand{\dd}[1]{\operatorname{d}^{#1}\mathopen{}}
\newcommand{\df}[2]{ {\f{\d #1}{\d #2}}}
\newcommand{\ds}[2]{ {\sl{\d #1}{\d #2}}}
\newcommand{\ddf}[3]{ {\f{\dd{#1} #2}{\p{\d #3}^{#1}}}}
\newcommand{\dds}[3]{ {\sl{\dd{#1} #2}{\p{\d #3}^{#1}}}}
\renewcommand{\part}{\partial}
\newcommand{\ppart}[1]{\part^{#1}}
\newcommand{\partf}[2]{\f{\part #1}{\part #2}}
\newcommand{\parts}[2]{\sl{\part #1}{\part #2}}
\newcommand{\ppartf}[3]{ {\f{\ppart{#1} #2}{\p{\part #3}^{#1}}}}
\newcommand{\pparts}[3]{ {\sl{\ppart{#1} #2}{\p{\part #3}^{#1}}}}
\newcommand{\grad}[1]{\mathop{\nabla\!_{#1}}}
% .. sets
\newcommand{\es}{\emptyset}
\newcommand{\N}{\mathbb{N}}
\newcommand{\Z}{\mathbb{Z}}
\newcommand{\R}{\mathbb{R}}
\newcommand{\Rge}{\R_{\ge 0}}
\newcommand{\Rgt}{\R_{> 0}}
\newcommand{\C}{\mathbb{C}}
\newcommand{\F}{\mathbb{F}}
\newcommand{\zo}{\set{0,1}}
\newcommand{\pmo}{\set{\pm 1}}
\newcommand{\zpmo}{\set{0,\pm 1}}
% .... set operations
\newcommand{\sse}{\subseteq}
\newcommand{\out}{\not\in}
\newcommand{\minus}{\setminus}
\newcommand{\inc}[1]{\union \set{#1}} % "including"
\newcommand{\exc}[1]{\setminus \set{#1}} % "except"
% .. over and under
\renewcommand{\ss}[1]{_{\substack{#1}}}
\newcommand{\OB}{\overbrace}
\newcommand{\ob}[2]{\OB{#1}^\t{#2}}
\newcommand{\UB}{\underbrace}
\newcommand{\ub}[2]{\UB{#1}_\t{#2}}
\newcommand{\ol}{\overline}
\newcommand{\tld}{\widetilde} % deprecated
\renewcommand{\~}{\widetilde}
\newcommand{\HAT}{\widehat} % deprecated
\renewcommand{\^}{\widehat}
\newcommand{\rt}[1]{ {\sqrt{#1}}}
\newcommand{\for}[2]{_{#1=1}^{#2}}
\newcommand{\sfor}{\sum\for}
\newcommand{\pfor}{\prod\for}
% .... two-part
\newcommand{\f}{\frac}
\renewcommand{\sl}[2]{#1 /\mathopen{}#2}
\newcommand{\ff}[2]{\mathchoice{\begin{smallmatrix}\displaystyle\vphantom{\p{#1}}#1\\[-0.05em]\hline\\[-0.05em]\hline\displaystyle\vphantom{\p{#2}}#2\end{smallmatrix}}{\begin{smallmatrix}\vphantom{\p{#1}}#1\\[-0.1em]\hline\\[-0.1em]\hline\vphantom{\p{#2}}#2\end{smallmatrix}}{\begin{smallmatrix}\vphantom{\p{#1}}#1\\[-0.1em]\hline\\[-0.1em]\hline\vphantom{\p{#2}}#2\end{smallmatrix}}{\begin{smallmatrix}\vphantom{\p{#1}}#1\\[-0.1em]\hline\\[-0.1em]\hline\vphantom{\p{#2}}#2\end{smallmatrix}}}
% .. arrows
\newcommand{\from}{\leftarrow}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\<}{\!\;\longleftarrow\;\!}
\let\>\undefined
\DeclareMathOperator*{\>}{\!\;\longrightarrow\;\!}
\let\-\undefined
\DeclareMathOperator*{\-}{\!\;\longleftrightarrow\;\!}
\newcommand{\so}{\implies}
% .. operators and relations
\renewcommand{\*}{\cdot}
\newcommand{\x}{\times}
\newcommand{\ox}{\otimes}
\newcommand{\OX}[1]{^{\ox #1}}
\newcommand{\sr}{\stackrel}
\newcommand{\ce}{\coloneqq}
\newcommand{\ec}{\eqqcolon}
\newcommand{\ap}{\approx}
\newcommand{\ls}{\lesssim}
\newcommand{\gs}{\gtrsim}
% .. punctuation and spacing
\renewcommand{\.}[1]{#1\dots#1}
\newcommand{\ts}{\thinspace}
\newcommand{\q}{\quad}
\newcommand{\qq}{\qquad}
%
%
%%% SPECIALIZED MATH %%%
%
% Logic and bit operations
\newcommand{\fa}{\forall}
\newcommand{\ex}{\exists}
\renewcommand{\and}{\wedge}
\newcommand{\AND}{\bigwedge}
\renewcommand{\or}{\vee}
\newcommand{\OR}{\bigvee}
\newcommand{\xor}{\oplus}
\newcommand{\XOR}{\bigoplus}
\newcommand{\union}{\cup}
\newcommand{\dunion}{\sqcup}
\newcommand{\inter}{\cap}
\newcommand{\UNION}{\bigcup}
\newcommand{\DUNION}{\bigsqcup}
\newcommand{\INTER}{\bigcap}
\newcommand{\comp}{\overline}
\newcommand{\true}{\r{true}}
\newcommand{\false}{\r{false}}
\newcommand{\tf}{\set{\true,\false}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\One}{\mathbb{1}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\1}{\mathbb{1}} % use \mathbbm instead if using real LaTeX
\DeclareMathOperator{\LSB}{LSB}
%
% Linear algebra
\newcommand{\spn}{\mathrm{span}} % do NOT use \span because it causes misery with amsmath
\DeclareMathOperator{\rank}{rank}
\DeclareMathOperator{\proj}{proj}
\DeclareMathOperator{\dom}{dom}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Img}{Im}
\DeclareMathOperator{\tr}{tr}
\DeclareMathOperator{\perm}{perm}
\DeclareMathOperator{\haf}{haf}
\newcommand{\transp}{\mathsf{T}}
\newcommand{\T}{^\transp}
\newcommand{\par}{\parallel}
% .. named tensors
\newcommand{\namedtensorstrut}{\vphantom{fg}} % milder than \mathstrut
\newcommand{\name}[1]{\mathsf{\namedtensorstrut #1}}
\newcommand{\nbin}[2]{\mathbin{\underset{\substack{#1}}{\namedtensorstrut #2}}}
\newcommand{\ndot}[1]{\nbin{#1}{\odot}}
\newcommand{\ncat}[1]{\nbin{#1}{\oplus}}
\newcommand{\nsum}[1]{\sum\limits_{\substack{#1}}}
\newcommand{\nfun}[2]{\mathop{\underset{\substack{#1}}{\namedtensorstrut\mathrm{#2}}}}
\newcommand{\ndef}[2]{\newcommand{#1}{\name{#2}}}
\newcommand{\nt}[1]{^{\transp(#1)}}
%
% Probability
\newcommand{\tri}{\triangle}
\newcommand{\Normal}{\mathcal{N}}
\newcommand{\Exp}{\mathcal{Exp}}
% .. operators
\DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp}
\let\Pr\undefined
\DeclareMathOperator*{\Pr}{Pr}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\G}{\mathbb{G}}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\Odds}{Od}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\E}{E}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\Var}{Var}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\Cov}{Cov}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\K}{K}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\corr}{corr}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\median}{median}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\maj}{maj}
% ... information theory
\let\H\undefined
\DeclareMathOperator*{\H}{H}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\I}{I}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\D}{D}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\KL}{KL}
% .. other divergences
\newcommand{\dTV}{d_{\mathrm{TV}}}
\newcommand{\dHel}{d_{\mathrm{Hel}}}
\newcommand{\dJS}{d_{\mathrm{JS}}}
%
% Polynomials
\DeclareMathOperator{\He}{He}
\DeclareMathOperator{\coeff}{coeff}
%
%%% SPECIALIZED COMPUTER SCIENCE %%%
%
% Complexity classes
% .. keywords
\newcommand{\coclass}{\mathsf{co}}
\newcommand{\Prom}{\mathsf{Promise}}
% .. classical
\newcommand{\PTIME}{\mathsf{P}}
\newcommand{\NP}{\mathsf{NP}}
\newcommand{\coNP}{\coclass\NP}
\newcommand{\PH}{\mathsf{PH}}
\newcommand{\PSPACE}{\mathsf{PSPACE}}
\renewcommand{\L}{\mathsf{L}}
\newcommand{\EXP}{\mathsf{EXP}}
\newcommand{\NEXP}{\mathsf{NEXP}}
% .. probabilistic
\newcommand{\formost}{\mathsf{Я}}
\newcommand{\RP}{\mathsf{RP}}
\newcommand{\BPP}{\mathsf{BPP}}
\newcommand{\ZPP}{\mathsf{ZPP}}
\newcommand{\MA}{\mathsf{MA}}
\newcommand{\AM}{\mathsf{AM}}
\newcommand{\IP}{\mathsf{IP}}
\newcommand{\RL}{\mathsf{RL}}
% .. circuits
\newcommand{\NC}{\mathsf{NC}}
\newcommand{\AC}{\mathsf{AC}}
\newcommand{\ACC}{\mathsf{ACC}}
\newcommand{\ThrC}{\mathsf{TC}}
\newcommand{\Ppoly}{\mathsf{P}/\poly}
\newcommand{\Lpoly}{\mathsf{L}/\poly}
% .. resources
\newcommand{\TIME}{\mathsf{TIME}}
\newcommand{\NTIME}{\mathsf{NTIME}}
\newcommand{\SPACE}{\mathsf{SPACE}}
\newcommand{\TISP}{\mathsf{TISP}}
\newcommand{\SIZE}{\mathsf{SIZE}}
% .. custom
\newcommand{\NCP}{\mathsf{NCP}}
%
% Boolean analysis
\newcommand{\harpoon}{\!\upharpoonright\!}
\newcommand{\rr}[2]{#1\harpoon_{#2}}
\newcommand{\Fou}[1]{\widehat{#1}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Ind}{\mathrm{Ind}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Inf}{\mathrm{Inf}}
\newcommand{\Der}[1]{\operatorname{D}_{#1}\mathopen{}}
% \newcommand{\Exp}[1]{\operatorname{E}_{#1}\mathopen{}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Stab}{\mathrm{Stab}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Tau}{T}
\DeclareMathOperator{\sens}{\mathrm{s}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\bsens}{\mathrm{bs}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\fbsens}{\mathrm{fbs}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Cert}{\mathrm{C}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\DT}{\mathrm{DT}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\CDT}{\mathrm{CDT}} % canonical
\DeclareMathOperator{\ECDT}{\mathrm{ECDT}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\CDTv}{\mathrm{CDT_{vars}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\ECDTv}{\mathrm{ECDT_{vars}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\CDTt}{\mathrm{CDT_{terms}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\ECDTt}{\mathrm{ECDT_{terms}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\CDTw}{\mathrm{CDT_{weighted}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\ECDTw}{\mathrm{ECDT_{weighted}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\AvgDT}{\mathrm{AvgDT}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\PDT}{\mathrm{PDT}} % partial decision tree
\DeclareMathOperator{\DTsize}{\mathrm{DT_{size}}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\W}{\mathbf{W}}
% .. functions (small caps sadly doesn't work)
\DeclareMathOperator{\Par}{\mathrm{Par}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Maj}{\mathrm{Maj}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\HW}{\mathrm{HW}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Thr}{\mathrm{Thr}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\Tribes}{\mathrm{Tribes}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\RotTribes}{\mathrm{RotTribes}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\CycleRun}{\mathrm{CycleRun}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\SAT}{\mathrm{SAT}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\UniqueSAT}{\mathrm{UniqueSAT}}
%
% Dynamic optimality
\newcommand{\OPT}{\mathsf{OPT}}
\newcommand{\Alt}{\mathsf{Alt}}
\newcommand{\Funnel}{\mathsf{Funnel}}
%
% Alignment
\DeclareMathOperator{\Amp}{\mathrm{Amp}}
%
%%% TYPESETTING %%%
%
% In "text"
\newcommand{\heart}{\heartsuit}
\newcommand{\nth}{^\t{th}}
\newcommand{\degree}{^\circ}
\newcommand{\qu}[1]{\text{``}#1\text{''}}
% remove these last two if using real LaTeX
\newcommand{\qed}{\blacksquare}
\newcommand{\qedhere}{\tag*{$\blacksquare$}}
%
% Fonts
% .. bold
\newcommand{\BA}{\boldsymbol{A}}
\newcommand{\BB}{\boldsymbol{B}}
\newcommand{\BC}{\boldsymbol{C}}
\newcommand{\BD}{\boldsymbol{D}}
\newcommand{\BE}{\boldsymbol{E}}
\newcommand{\BF}{\boldsymbol{F}}
\newcommand{\BG}{\boldsymbol{G}}
\newcommand{\BH}{\boldsymbol{H}}
\newcommand{\BI}{\boldsymbol{I}}
\newcommand{\BJ}{\boldsymbol{J}}
\newcommand{\BK}{\boldsymbol{K}}
\newcommand{\BL}{\boldsymbol{L}}
\newcommand{\BM}{\boldsymbol{M}}
\newcommand{\BN}{\boldsymbol{N}}
\newcommand{\BO}{\boldsymbol{O}}
\newcommand{\BP}{\boldsymbol{P}}
\newcommand{\BQ}{\boldsymbol{Q}}
\newcommand{\BR}{\boldsymbol{R}}
\newcommand{\BS}{\boldsymbol{S}}
\newcommand{\BT}{\boldsymbol{T}}
\newcommand{\BU}{\boldsymbol{U}}
\newcommand{\BV}{\boldsymbol{V}}
\newcommand{\BW}{\boldsymbol{W}}
\newcommand{\BX}{\boldsymbol{X}}
\newcommand{\BY}{\boldsymbol{Y}}
\newcommand{\BZ}{\boldsymbol{Z}}
\newcommand{\Ba}{\boldsymbol{a}}
\newcommand{\Bb}{\boldsymbol{b}}
\newcommand{\Bc}{\boldsymbol{c}}
\newcommand{\Bd}{\boldsymbol{d}}
\newcommand{\Be}{\boldsymbol{e}}
\newcommand{\Bf}{\boldsymbol{f}}
\newcommand{\Bg}{\boldsymbol{g}}
\newcommand{\Bh}{\boldsymbol{h}}
\newcommand{\Bi}{\boldsymbol{i}}
\newcommand{\Bj}{\boldsymbol{j}}
\newcommand{\Bk}{\boldsymbol{k}}
\newcommand{\Bl}{\boldsymbol{l}}
\newcommand{\Bm}{\boldsymbol{m}}
\newcommand{\Bn}{\boldsymbol{n}}
\newcommand{\Bo}{\boldsymbol{o}}
\newcommand{\Bp}{\boldsymbol{p}}
\newcommand{\Bq}{\boldsymbol{q}}
\newcommand{\Br}{\boldsymbol{r}}
\newcommand{\Bs}{\boldsymbol{s}}
\newcommand{\Bt}{\boldsymbol{t}}
\newcommand{\Bu}{\boldsymbol{u}}
\newcommand{\Bv}{\boldsymbol{v}}
\newcommand{\Bw}{\boldsymbol{w}}
\newcommand{\Bx}{\boldsymbol{x}}
\newcommand{\By}{\boldsymbol{y}}
\newcommand{\Bz}{\boldsymbol{z}}
\newcommand{\Balpha}{\boldsymbol{\alpha}}
\newcommand{\Bbeta}{\boldsymbol{\beta}}
\newcommand{\Bgamma}{\boldsymbol{\gamma}}
\newcommand{\Bdelta}{\boldsymbol{\delta}}
\newcommand{\Beps}{\boldsymbol{\eps}}
\newcommand{\Bveps}{\boldsymbol{\veps}}
\newcommand{\Bzeta}{\boldsymbol{\zeta}}
\newcommand{\Beta}{\boldsymbol{\eta}}
\newcommand{\Btheta}{\boldsymbol{\theta}}
\newcommand{\Bth}{\boldsymbol{\th}}
\newcommand{\Biota}{\boldsymbol{\iota}}
\newcommand{\Bkappa}{\boldsymbol{\kappa}}
\newcommand{\Blambda}{\boldsymbol{\lambda}}
\newcommand{\Bmu}{\boldsymbol{\mu}}
\newcommand{\Bnu}{\boldsymbol{\nu}}
\newcommand{\Bxi}{\boldsymbol{\xi}}
\newcommand{\Bpi}{\boldsymbol{\pi}}
\newcommand{\Bvpi}{\boldsymbol{\vpi}}
\newcommand{\Brho}{\boldsymbol{\rho}}
\newcommand{\Bsigma}{\boldsymbol{\sigma}}
\newcommand{\Btau}{\boldsymbol{\tau}}
\newcommand{\Bupsilon}{\boldsymbol{\upsilon}}
\newcommand{\Bphi}{\boldsymbol{\phi}}
\newcommand{\Bfi}{\boldsymbol{\fi}}
\newcommand{\Bchi}{\boldsymbol{\chi}}
\newcommand{\Bpsi}{\boldsymbol{\psi}}
\newcommand{\Bom}{\boldsymbol{\om}}
% .. calligraphic
\newcommand{\CA}{\mathcal{A}}
\newcommand{\CB}{\mathcal{B}}
\newcommand{\CC}{\mathcal{C}}
\newcommand{\CD}{\mathcal{D}}
\newcommand{\CE}{\mathcal{E}}
\newcommand{\CF}{\mathcal{F}}
\newcommand{\CG}{\mathcal{G}}
\newcommand{\CH}{\mathcal{H}}
\newcommand{\CI}{\mathcal{I}}
\newcommand{\CJ}{\mathcal{J}}
\newcommand{\CK}{\mathcal{K}}
\newcommand{\CL}{\mathcal{L}}
\newcommand{\CM}{\mathcal{M}}
\newcommand{\CN}{\mathcal{N}}
\newcommand{\CO}{\mathcal{O}}
\newcommand{\CP}{\mathcal{P}}
\newcommand{\CQ}{\mathcal{Q}}
\newcommand{\CR}{\mathcal{R}}
\newcommand{\CS}{\mathcal{S}}
\newcommand{\CT}{\mathcal{T}}
\newcommand{\CU}{\mathcal{U}}
\newcommand{\CV}{\mathcal{V}}
\newcommand{\CW}{\mathcal{W}}
\newcommand{\CX}{\mathcal{X}}
\newcommand{\CY}{\mathcal{Y}}
\newcommand{\CZ}{\mathcal{Z}}
% .. typewriter
\newcommand{\TA}{\mathtt{A}}
\newcommand{\TB}{\mathtt{B}}
\newcommand{\TC}{\mathtt{C}}
\newcommand{\TD}{\mathtt{D}}
\newcommand{\TE}{\mathtt{E}}
\newcommand{\TF}{\mathtt{F}}
\newcommand{\TG}{\mathtt{G}}
\renewcommand{\TH}{\mathtt{H}}
\newcommand{\TI}{\mathtt{I}}
\newcommand{\TJ}{\mathtt{J}}
\newcommand{\TK}{\mathtt{K}}
\newcommand{\TL}{\mathtt{L}}
\newcommand{\TM}{\mathtt{M}}
\newcommand{\TN}{\mathtt{N}}
\newcommand{\TO}{\mathtt{O}}
\newcommand{\TP}{\mathtt{P}}
\newcommand{\TQ}{\mathtt{Q}}
\newcommand{\TR}{\mathtt{R}}
\newcommand{\TS}{\mathtt{S}}
\newcommand{\TT}{\mathtt{T}}
\newcommand{\TU}{\mathtt{U}}
\newcommand{\TV}{\mathtt{V}}
\newcommand{\TW}{\mathtt{W}}
\newcommand{\TX}{\mathtt{X}}
\newcommand{\TY}{\mathtt{Y}}
\newcommand{\TZ}{\mathtt{Z}}
%
% LEVELS OF CLOSENESS (basically deprecated)
\newcommand{\scirc}[1]{\sr{\circ}{#1}}
\newcommand{\sdot}[1]{\sr{.}{#1}}
\newcommand{\slog}[1]{\sr{\log}{#1}}
\newcommand{\createClosenessLevels}[7]{
\newcommand{#2}{\mathrel{(#1)}}
\newcommand{#3}{\mathrel{#1}}
\newcommand{#4}{\mathrel{#1\!\!#1}}
\newcommand{#5}{\mathrel{#1\!\!#1\!\!#1}}
\newcommand{#6}{\mathrel{(\sdot{#1})}}
\newcommand{#7}{\mathrel{(\slog{#1})}}
}
\let\lt\undefined
\let\gt\undefined
% .. vanilla versions (is it within a constant?)
\newcommand{\ez}{\scirc=}
\newcommand{\eq}{\simeq}
\newcommand{\eqq}{\mathrel{\eq\!\!\eq}}
\newcommand{\eqqq}{\mathrel{\eq\!\!\eq\!\!\eq}}
\newcommand{\lez}{\scirc\le}
\renewcommand{\lq}{\preceq}
\newcommand{\lqq}{\mathrel{\lq\!\!\lq}}
\newcommand{\lqqq}{\mathrel{\lq\!\!\lq\!\!\lq}}
\newcommand{\gez}{\scirc\ge}
\newcommand{\gq}{\succeq}
\newcommand{\gqq}{\mathrel{\gq\!\!\gq}}
\newcommand{\gqqq}{\mathrel{\gq\!\!\gq\!\!\gq}}
\newcommand{\lz}{\scirc<}
\newcommand{\lt}{\prec}
\newcommand{\ltt}{\mathrel{\lt\!\!\lt}}
\newcommand{\lttt}{\mathrel{\lt\!\!\lt\!\!\lt}}
\newcommand{\gz}{\scirc>}
\newcommand{\gt}{\succ}
\newcommand{\gtt}{\mathrel{\gt\!\!\gt}}
\newcommand{\gttt}{\mathrel{\gt\!\!\gt\!\!\gt}}
% .. dotted versions (is it equal in the limit?)
\newcommand{\ed}{\sdot=}
\newcommand{\eqd}{\sdot\eq}
\newcommand{\eqqd}{\sdot\eqq}
\newcommand{\eqqqd}{\sdot\eqqq}
\newcommand{\led}{\sdot\le}
\newcommand{\lqd}{\sdot\lq}
\newcommand{\lqqd}{\sdot\lqq}
\newcommand{\lqqqd}{\sdot\lqqq}
\newcommand{\ged}{\sdot\ge}
\newcommand{\gqd}{\sdot\gq}
\newcommand{\gqqd}{\sdot\gqq}
\newcommand{\gqqqd}{\sdot\gqqq}
\newcommand{\ld}{\sdot<}
\newcommand{\ltd}{\sdot\lt}
\newcommand{\lttd}{\sdot\ltt}
\newcommand{\ltttd}{\sdot\lttt}
\newcommand{\gd}{\sdot>}
\newcommand{\gtd}{\sdot\gt}
\newcommand{\gttd}{\sdot\gtt}
\newcommand{\gtttd}{\sdot\gttt}
% .. log versions (is it equal up to log?)
\newcommand{\elog}{\slog=}
\newcommand{\eqlog}{\slog\eq}
\newcommand{\eqqlog}{\slog\eqq}
\newcommand{\eqqqlog}{\slog\eqqq}
\newcommand{\lelog}{\slog\le}
\newcommand{\lqlog}{\slog\lq}
\newcommand{\lqqlog}{\slog\lqq}
\newcommand{\lqqqlog}{\slog\lqqq}
\newcommand{\gelog}{\slog\ge}
\newcommand{\gqlog}{\slog\gq}
\newcommand{\gqqlog}{\slog\gqq}
\newcommand{\gqqqlog}{\slog\gqqq}
\newcommand{\llog}{\slog<}
\newcommand{\ltlog}{\slog\lt}
\newcommand{\lttlog}{\slog\ltt}
\newcommand{\ltttlog}{\slog\lttt}
\newcommand{\glog}{\slog>}
\newcommand{\gtlog}{\slog\gt}
\newcommand{\gttlog}{\slog\gtt}
\newcommand{\gtttlog}{\slog\gttt}$
Model
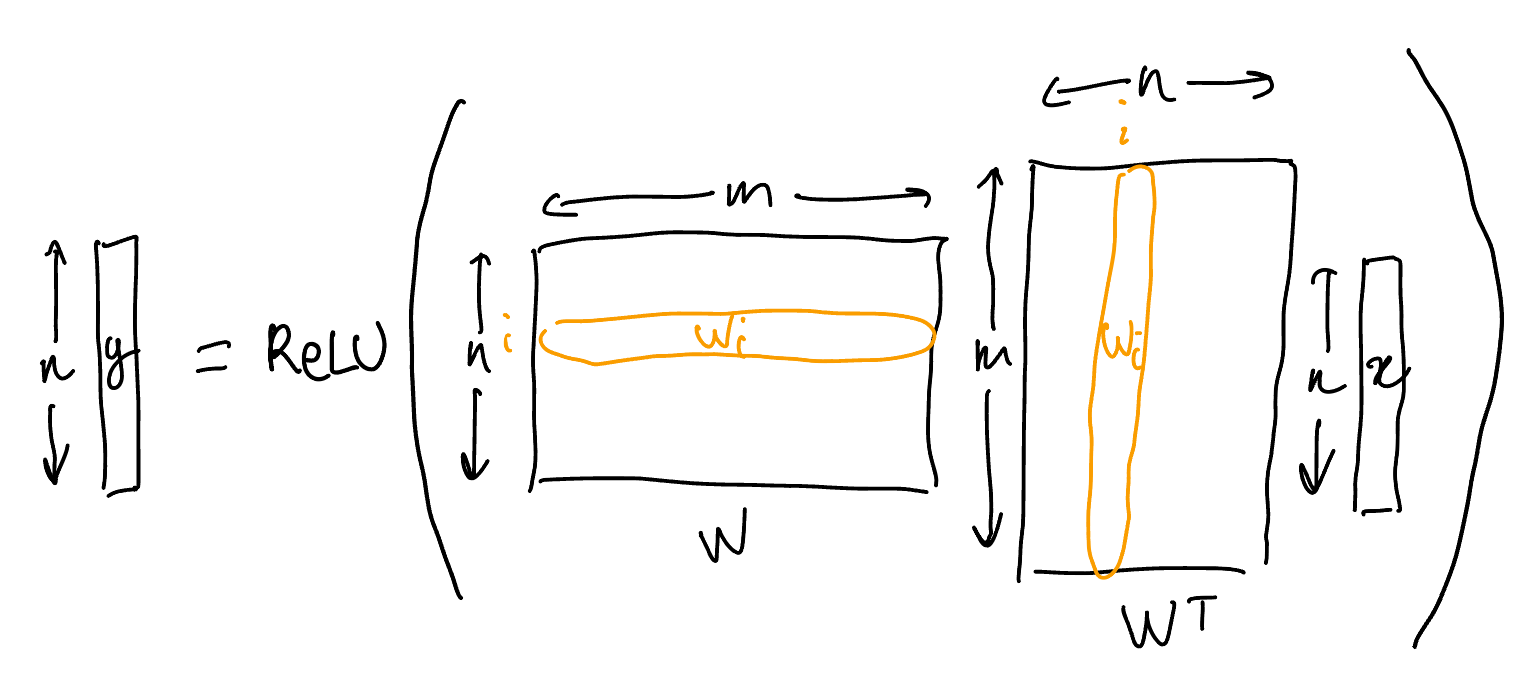
Consider an autoencoder with $n$ features which
- has weight tying between the encoder and the decoder (let $W \in \R^{n\times m}$ be those weights),
- uses a single hidden layer of size $m$ with $l_1$ regularization of strength $\lambda$ on the activations,
- has a ReLU on the output layer,
- has no biases anywhere,
- is trained with the $n$ standard basis vectors as data.
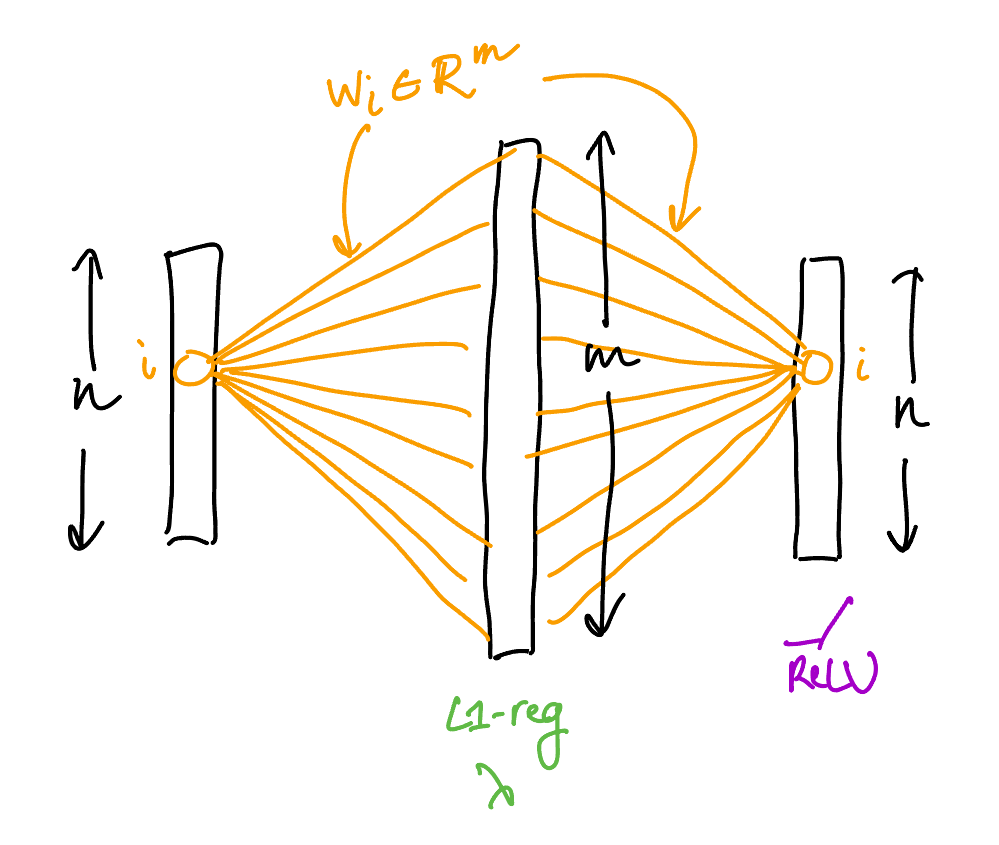
The output is computed as $\ReLU(WW^\transp x)$.
Assumptions and claims
Let’s make the following assumptions:
| # |
Assumption |
Reason |
| 1 |
the weights $W_{ik}$ are initialized to i.i.d. normals of mean $0$ and standard deviation $\frac{1}{100\sqrt{m}}$ |
so that the encodings $W_i \in \R^m$ start out with constant length but not too close to $1$ |
| 2 |
$m >\omega(n)$ |
so that the interference is not too strong initially, and also $m\ge n$ makes it clear that polysemanticity is not necessary |
| 3 |
$\lambda \sqrt{m} < o(n/m)$ |
so that the $l_1$ regularization is initially the weakest force |
Then we claim that the training will roughly go through the following “phases”. They’re all overlapping, but some of them vary based on how much time they take to have a significant effect.
- The encodings $W_i \in \R^m$ will grow/shrink to have unit length.
- Any encodings $W_i$, $W_j$ that have positive inner product will repulse each other until their inner product is $0$ (but none of them will move very significantly).
- The smaller coordinates of each $W_i$ (in absolute value) will progressively all drop to $0$ while the bigger ones increase, until only one remains, with absolute value $\approx 1$. For two encodings $W_i$ and $W_j$, when there is a $k$ such that $W_{ik}$ is among the largest entries of $W_i$ and $W_{jk}$ is among the largest entries of $W_j$, then
- if $W_{ik}$ and $W_{jk}$ have the same sign, this will cause large interference and at least one of them will have to drop,
- if $W_{ik}$ and $W_{jk}$ have opposite signs, this will not cause interference, and it mightt be the case that we have $|W_{ik}|, |W_{jk}| \approx 1$ by the end of training.
Loss and forces
The loss is
\[
\CL = \sum_i\p{\p{1-\norm{W_i}^2}^2 + \sum_{j \ne i}\ReLU(W_i \cdot W_j)^2 + \lambda\norm{W_i}_1},
\]
so the gradient is
\[
\frac{\d W_i}{\d t} \ce -\frac{\partial \CL}{\partial W_i} = 4\ \UB{\p{1-\norm{W_i}^2}W_i}_\text{feature benefit} - 4\ \UB{\sum_{j \ne i}\ReLU(W_i \cdot W_j)W_j}_\text{interference} - \UB{\lambda \ \sign(W_i)}_\text{regularization}
\]
(we’ll happily drop the constants $4$ going forward).
It can be decomposed into three intuitive “forces”:
- “feature benefit”: encodings want to have unit length;
- “interference”: encodings avoid pointing in similar directions;
- “regularization”: encodings want to have small $l_1$-norm, which pushes for sparsity since we’re constraining their $l_2$-norm to be $\approx 1$.
Of those:
- both feature benefit and interference are rotationally symmetric: their expression wouldn’t change if we applied the same rotation (in $\R^m$) to all the encodings;
- both feature benefit and regularization work on different encodings independently: the value of other encodings $W_j$ doesn’t affect how $W_i$ changes.
Because of this, it is fairly easy to study the effect of feature benefit combined with one of interference or regularization, but harder to consider interference and regularization together.
Strength at initialization
Let’s look at how strong each force on $W_i$ initially is. As it happens,
- feature benefit will be aligned with $W_i$,
- interference will be mostly aligned with $W_i$,
- regularization will be somewhat aligned with $W_i$, and definitely more aligned with $W_i$ than with any of the other encodings.
So we will compare them numerically by taking their inner product with $W_i$ itself, i.e. their contribution to
\[
\frac{\d W_i}{\d t} \cdot W_i,
\]
which intuitively captures the “parallel push” on $W_i$, or how much the length of $W_i$ is being affected.
Feature benefit
Initially, $\norm{W_i}$ will (x.w.p. $e^{-\Omega(m)}$) be a constant $<1/2$, so $1-\norm{W_i}^2 = \Theta(1)$, and the parallel push of the feature benefit force is
\[
\p{\p{1-\norm{W_i}^2}W_i}\cdot W_i = \p{1-\norm{W_i}^2}\norm{W_i}^2 = \Theta(1)\times\Theta(1) = \Theta(1).
\]
That is, feature benefit pushes $W_i$ up by a constant amount.
Interference
Since the sum $\sum_{j \ne i}\ReLU(W_i \cdot W_j)W_j$ is only adding each $W_j$ up if it is cosine-similar to $W_i$, the interference will mostly point in the same direction as $W_i$ (but opposing it).
We have
\[
\al{
\p{\sum_{j \ne i}\ReLU(W_i \cdot W_j)W_j} \cdot W_i
&= \sum_{j \ne i}\ReLU(W_i \cdot W_j)(W_i\cdot W_j)\\
&= \sum_{j \ne i}
\begin{cases}
(W_i \cdot W_j)^2 &\text{if $W_i \cdot W_j > 0$}\\
0&\text{otherwise.}
\end{cases}
}
\]
Now, $W_i \cdot W_j$ is a reasonable random variable with mean $0$ and std $\Theta\p{1/\sqrt{m}}$, so each term of this sum is a reasonable random variable with mean and std both $\Theta(1/m)$, so the sum itself will have mean $\Theta(n/m)$ and be concentrated.
This means interference pushes down on $W_i$ by an amount $\Theta(n/m)$, which by assumption #2 is sub-constant.
Regularization
The $l_1$ regularization pushes every coordinate of $W_i$ towards zero with equal force $\lambda$, so it will be somewhat aligned with $W_i$ in the sense that they have opposite signs for every coordinate. We have
\[
\p{\lambda\ \sign(W_i)} \cdot W_i = \lambda \sum_k |W_{ik}| = \lambda \norm{W_i}_1,
\]
and $|W_{ik}|$ has mean and standard deviation $\Theta\p{1/\sqrt{m}}$, so the $1$-norm $\norm{W_i}_1$ has mean $\Theta\p{\sqrt{m}}$ and is concentrated.
This means regularization pushes down on $W_i$ by an amount $\Theta\p{\lambda \sqrt{m}}$, which by assumption #3 is even smaller than the intereference push of $\Theta(n/m)$.
Summary
Initially, feature benefit overpowers interference, which overpowers regularization (by assumption #3).
| Force |
Parallel push |
| feature benefit |
$\Theta(1)$ |
| interference |
$\Theta(n/m)$ |
| regularization |
$\Theta\p{\lambda\sqrt{m}}$ |
“Phase 1”: grow to unit length
We have
\[
\frac{\d \p{\norm{W_i}^2}}{\d t} = 2\frac{\d W_i}{\d t} \cdot W_i
\]
and we already saw earlier that the contribution of the feature benefit force to $\frac{\d W_i}{\d t} \cdot W_i$ was $\Theta\p{\p{1-\norm{W_i}^2}\norm{W_i}^2}$, so as long as the feature benefit force dominates, we have
\[
\frac{\d \p{\norm{W_i}^2}}{\d t} \approx \Theta\p{\p{1-\norm{W_i}^2}\norm{W_i}^2} = \Theta\p{1-\norm{W_i}^2},
\]
which means that over time, the length of $W_i$ approaches $1$ at an exponential rate:
\[
\norm{W_i(t)}^2 \approx 1-e^{-\Theta(t)}.
\]
So for as long as feature benefit is the dominant force on $\norm{W_i}^2$, it would reach a value of $1-\eps$ at time $t \approx \log(1/\eps)$.
Note: In particular, after time $t \approx \log(m/n)$, the norm of $W_i$ will have reached $1-\Theta(n/m)$, at which point the feature benefit force becomes as weak as the interference in terms of parallel push. But I’m not sure yet if this is the most natural “cutoff point” between phase 1 and phase 2.
“Phase 2”: eliminate the interferences
See Feature benefit vs interference.
“Phase 3”: sparsify
Tug-of-war between feature benefit and regularization
See Feature benefit vs regularization.
Adding in interference
#to-write

